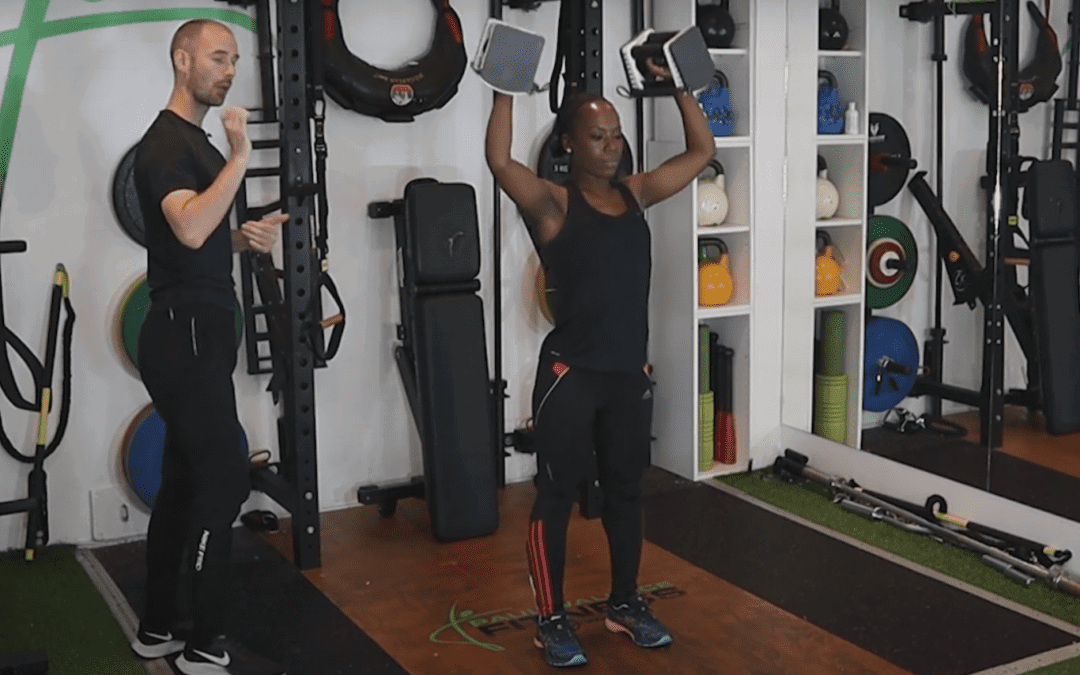
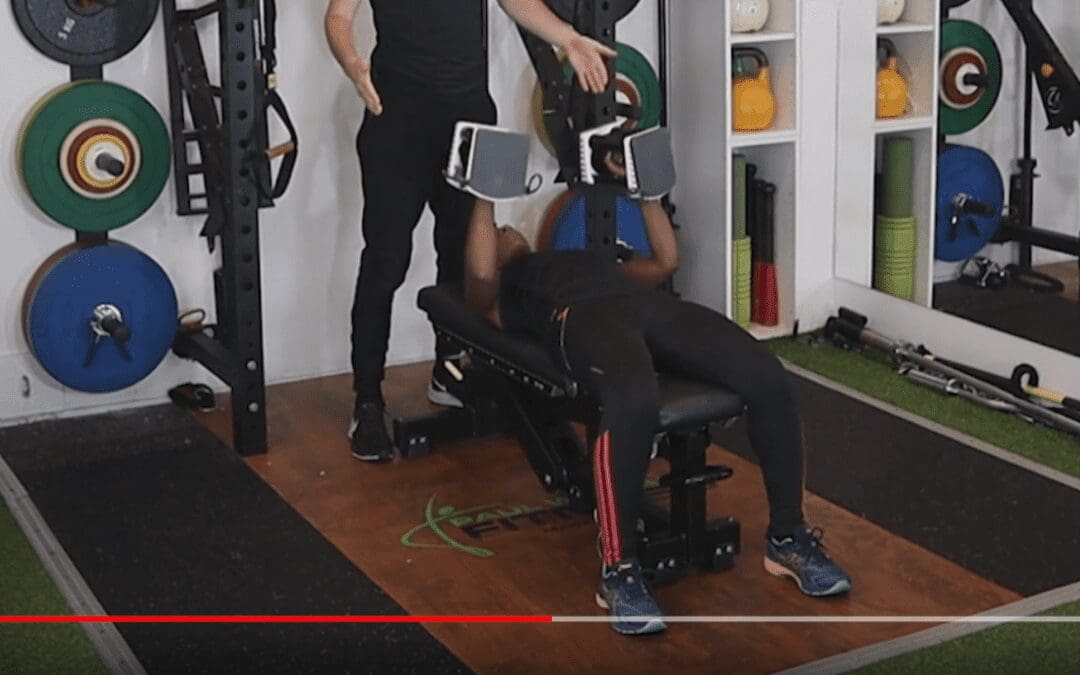
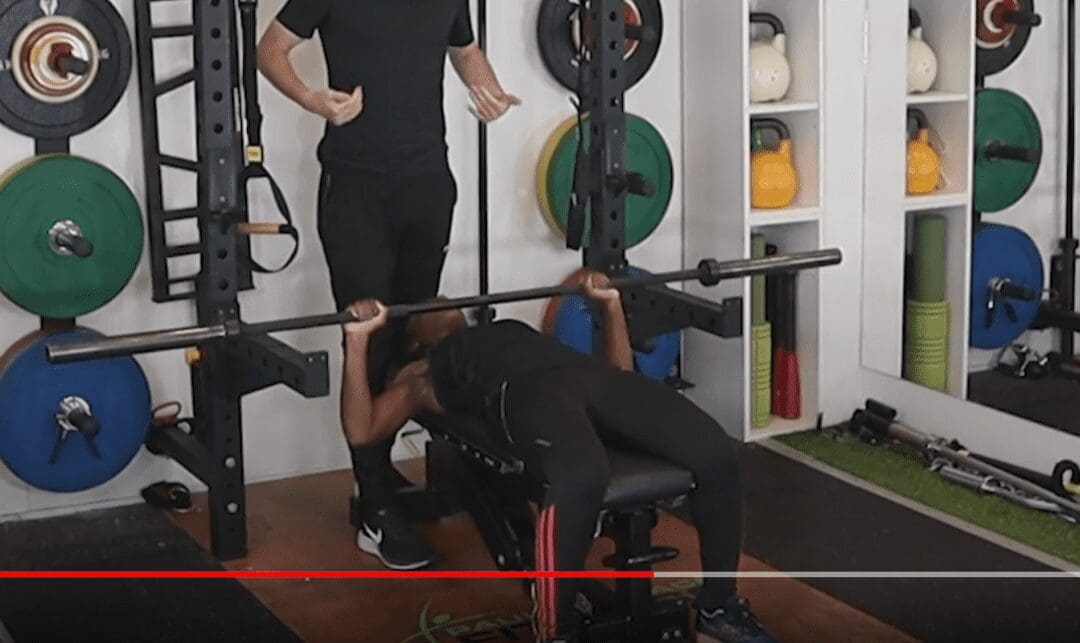
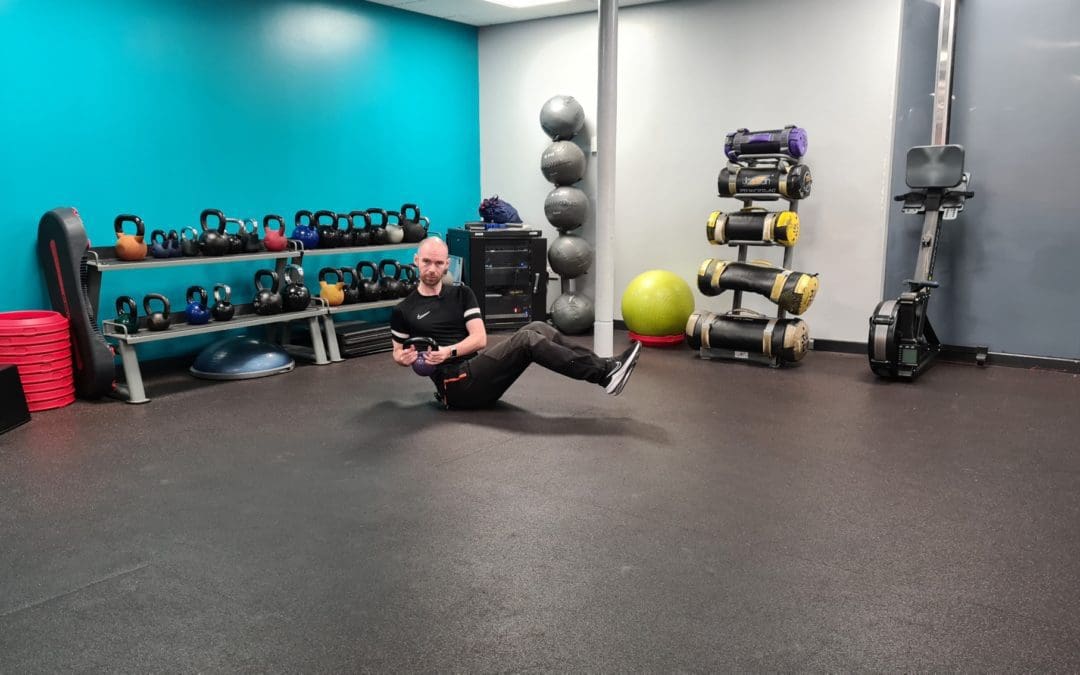
training.nutrition.mindset
the 90days lab
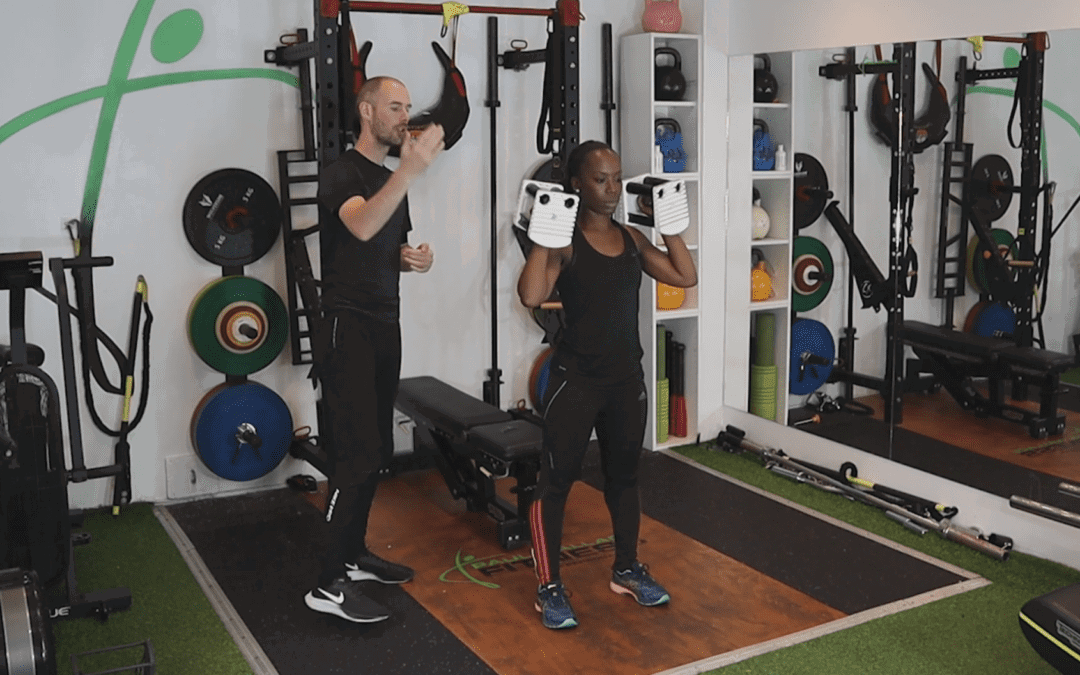
Intro
Video
Introduction and Goal-Setting
Target: Set realistic and achievable goals for the 12-week program, learn about the course, and track progress.
Modules:
- Course overview and objectives
- Importance of mindset and motivation
- Self-assessment and tracking progress
- Goal-setting strategies
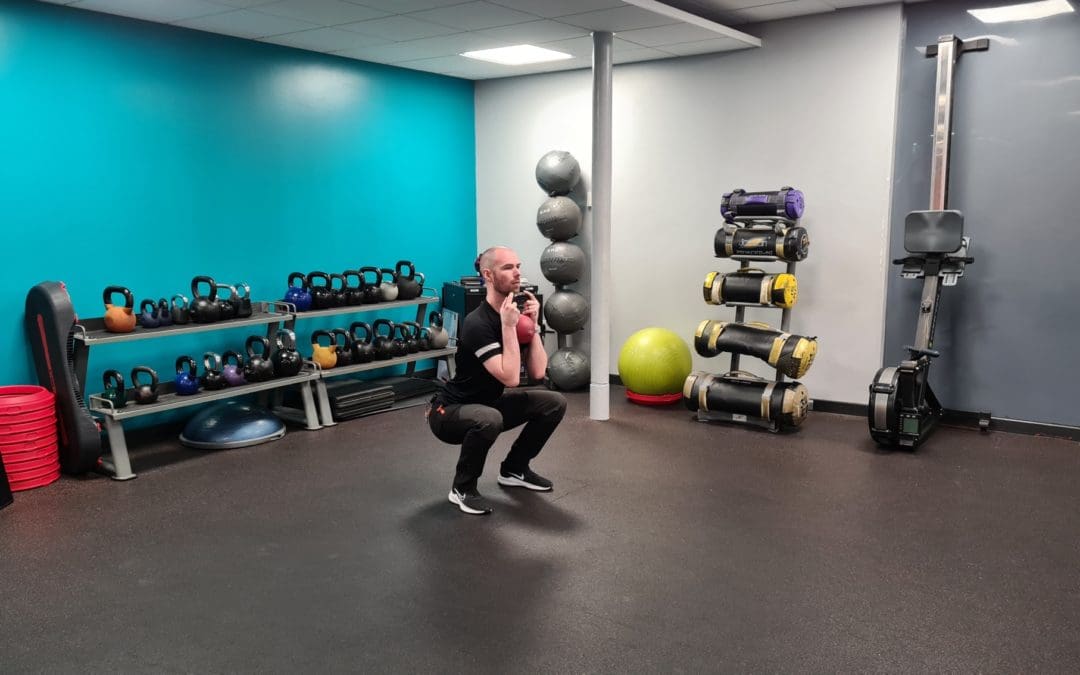
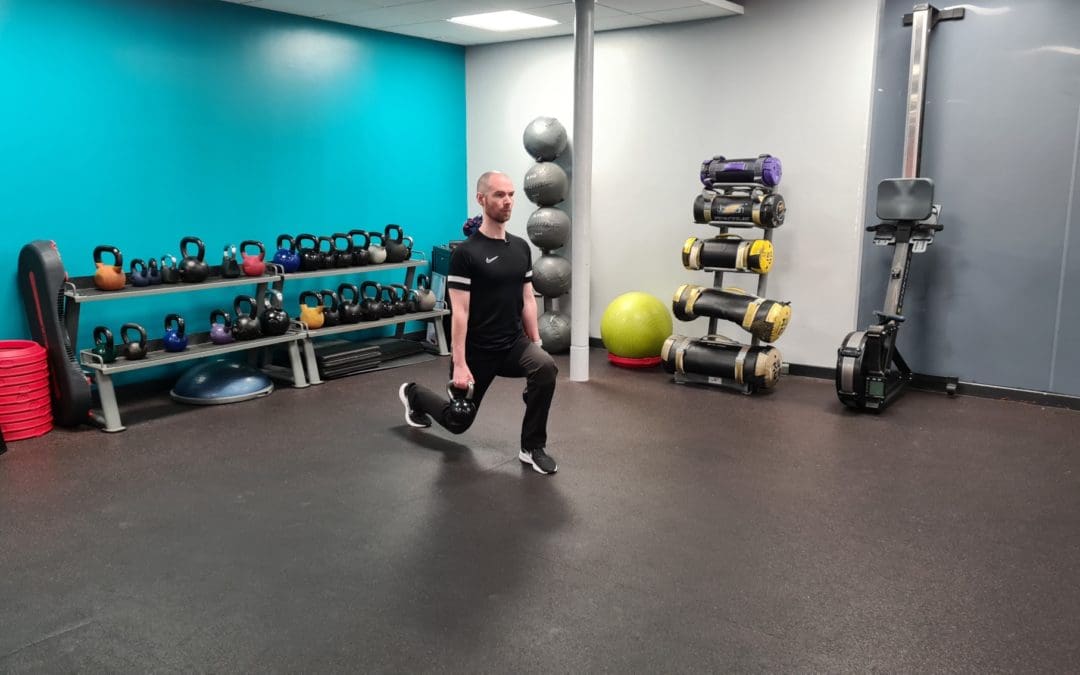
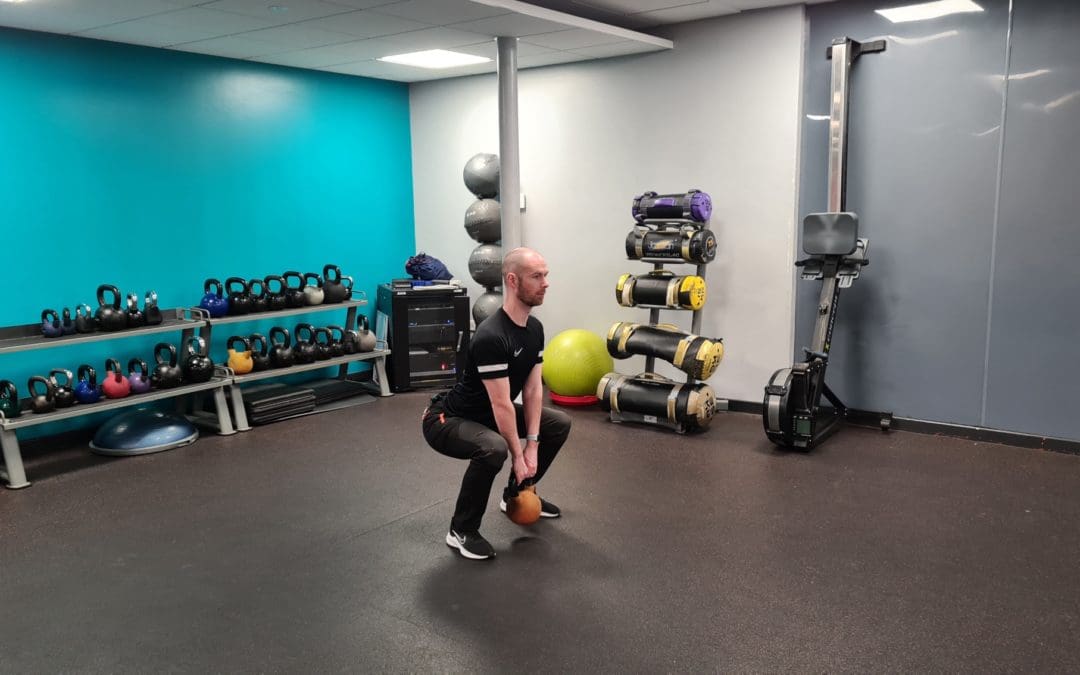
The First 30 Days
prepare to build better...
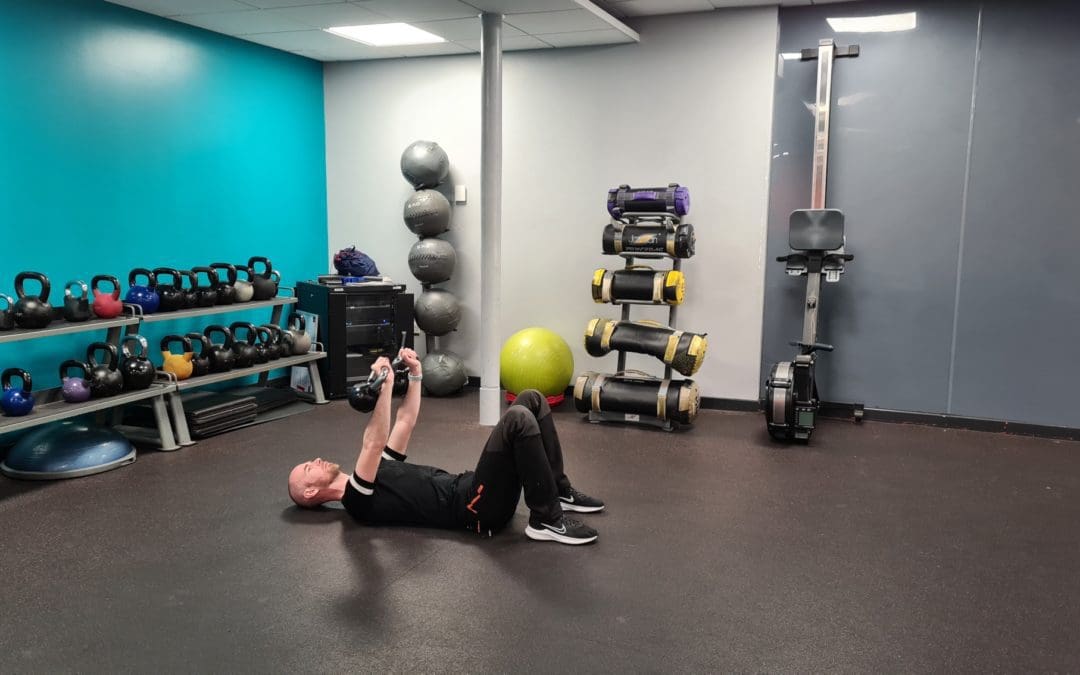
Nutrition Basics and Mindful Eating
Target: Learn about healthy eating habits, portion control, and mindful eating.
Modules:
- Introduction to macronutrients and micronutrients
- Understanding portion sizes
- Healthy food choices and substitutions
- Mindful eating and avoiding emotional eating
Meal Planning and Preparation
Target:Learn how to plan and prepare healthy meals, including tips for grocery shopping and budgeting.
Modules:
- Developing personalized meal plans
- Tips for grocery shopping and budgeting
- Recipe sharing and cooking demos
- Meal prep strategies
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
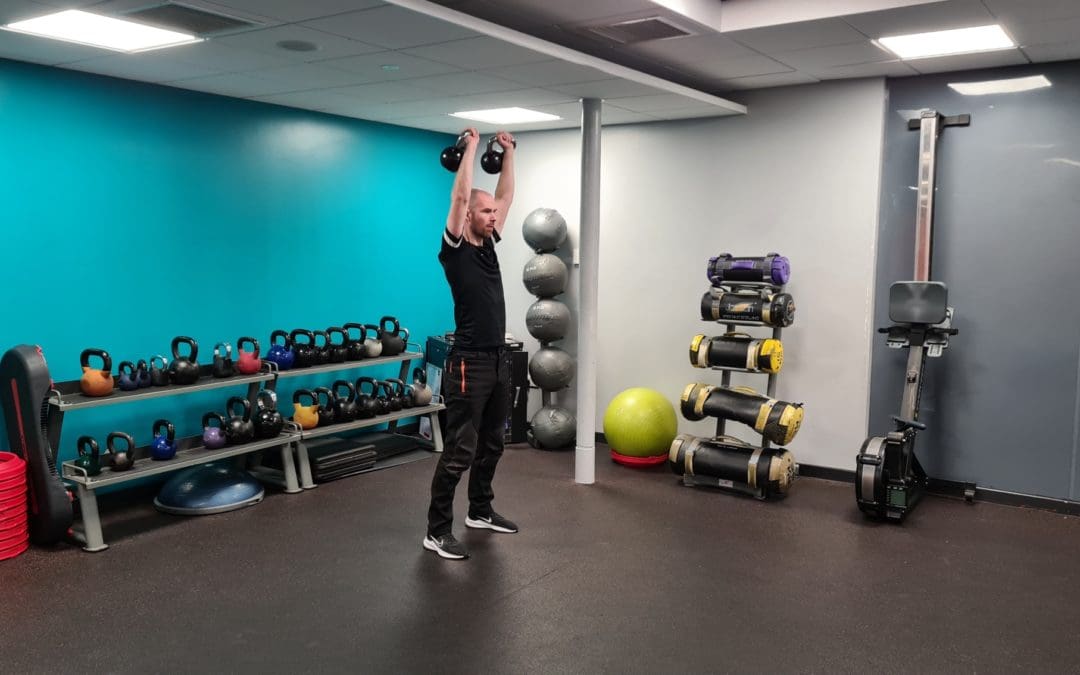
Nutrition and Exercise
Target: Understand the connection between food and exercise and learn how to fuel workouts with the right foods.
Modules:
- Understanding the connection between food and exercise
- Fueling workouts with the right foods
- Pre- and post-workout nutrition
- Avoiding common nutrition and exercise pitfalls
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Modules:
- Strategies for maintaining weight loss and healthy habits
- Coping with setbacks and slip-ups
- Setting long-term goals and priorities
- Living a balanced and fulfilling life
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Freeweights
Chest
Freeweights
Core
Freeweights
Shoulders (Back)
Freeweights
Hamstrings
Fixed
Chest
Fixed
Core
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Fixed
Quads
Fixed
Shoulders (Back)
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Fixed
Glutes
Fixed
Hamstrings
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
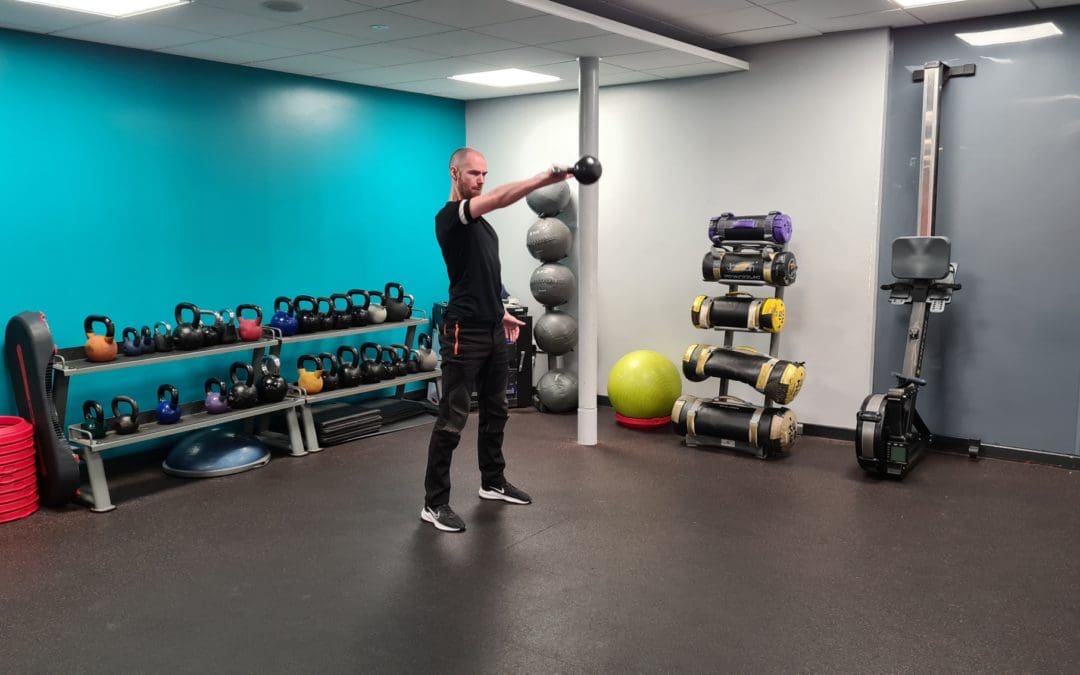
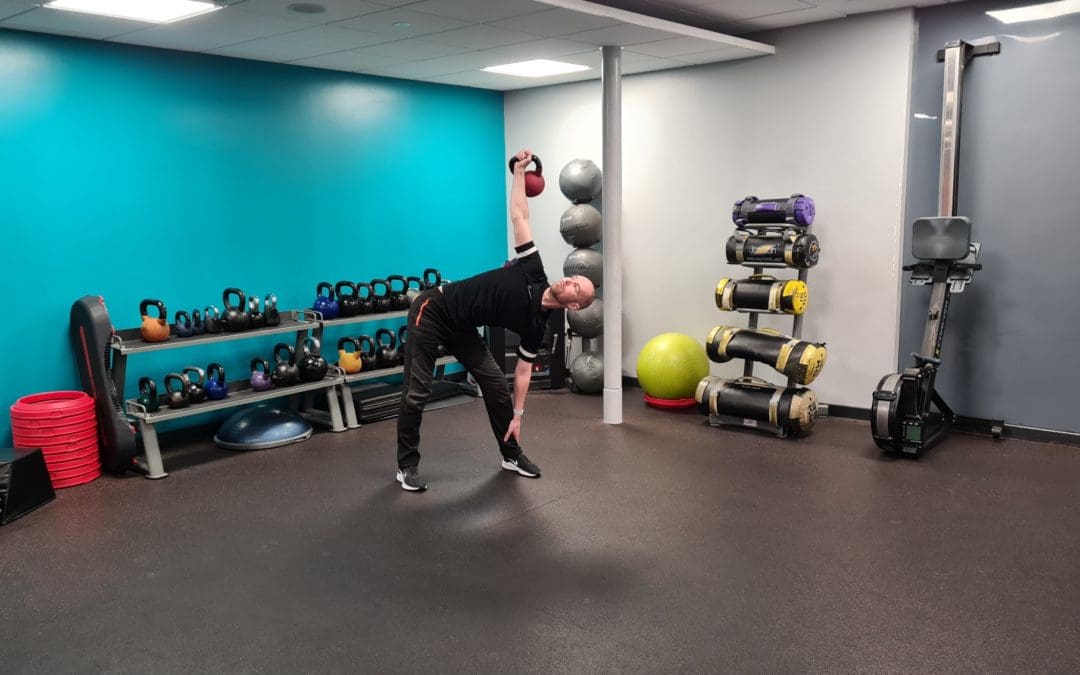
Kettlebells
Chest
Kettlebells
Core
Kettlebells
Shoulders (Back)
Kettlebells
Back
Kettlebells
Hamstrings
Accessories
Core
Accessories
Quads
Accessories
Shoulders (Back)
Accessories
Glutes
Accessories
Hamstrings
Abduction
Movement away from the body such as what occurs when you raise your arm straight out to the side.
Abs
A slang term referring to the abdominal muscles.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
The molecular “currency” that provides energy in cells for everything from protein synthesis to muscle contraction.
Adduction
Movement of a limb toward the body such as what occurs when your arm is straight out to your side and you lower it down to the side of your body.
Adipose Tissue
Where fat is stored in the body.
Advanced Weightlifter
A person who has strength-trained steadily and systematically for at least one full year.
Aerobic Exercise
Prolonged (usually per formed for at least 20 minutes continu ously), moderate-intensity exercise that uses up oxygen at or below the level at which the cardiorespiratory system can replenish oxygen in the working muscles. Common aerobic exercise activities are walking, jog ging, running, cycling, stair climbing, work ing out on elliptical exercise machines, rowing, swimming, dancing, and aerobic
Anterior
An anatomical term referring to the front of the body.
Anaerobic Exercise
Exercise that is higher in intensity than aerobic work. Anaerobic exer cise uses up oxygen more quickly than the body can replenish it in the working muscles. Anaerobic exercise uses stored-muscle ATP, phosphocreatine, and glycogen to supply its energy needs. Common anaerobic activities are weightlifting and sprinting,
Antagonist Muscle
The muscle responsible for actively opposing the concentric muscle action of the agonist muscle. Although this seems counterintuitive, the opposing force is necessary for joint stability during the movement. For example, during the biceps curl exercise, the triceps muscle is the antagonist muscle.
Assistance Exercise
Typically single-joint exer cises such as the biceps curl, triceps extension, and deltoid lateral raise. These exercises involve only a single muscle group.
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate Atrophy – Wasting away of any part, organ, tissue, or cell, such as the atrophy of muscle fibers caused by inactivity.
Belt
See “weight belt”
Bis
A slang term for the biceps muscles
Bodybuilding
A type of strength training applied in conjunction with nutritional practices to alter the shape of the body’s
Basal Metabolic Rate
The rate at which the body burns calories while awake but at rest (usually measured in calories per day).
Ballistic Stretch
This type of muscle stretch involves dynamic muscle action in which the muscles are stretched suddenly in a bouncing movement. A ballistic stretch for the hamstrings might involve touching your toes repeatedly in rapid succession.
BMR
See Basal Metabolic Rate
Beginning Weightlifter
A person with less than six months of strength training experience.
Burn
Body Fat Percentage
Bulking Up
Cardio
Chalk
Cheating
Compound Exercise
Cool-down
Cross-training
Cutting
Delayed
Delts
DOMS
Dorsiflexion
EPOC
Extension
Failure
False grip
Fast-twitch Muscle Fibers
Flexibility
Flexion
Form
GH
Gloves
Glutes
Glycogen
Growth hormone (GH)
Hypertrophy
Insertion
Intermediate Strength Trainer
Isolation Exercise
Knee Wrap
Knurling
Lean Body Mass
Lifter
Macrocycle
Mass
Mesocycle
Microcycle
Multijoint Exercise
Muscle Atrophy
Muscle Failure
Muscle Hypertrophy
Musculature
The sport of bodybuilding is a competitive sport in amateur and professional categories for males and females.
Negative Phase of Repetition
Olympic Weightlifting
Origin
Overhand grip
Overreaching
Overtraining
Passive Stretching
Peak
Pecs
Periodization
Phosphocreatine (PCR)
Plantar flexion
Positive Phase of Repetition
Powerlifting
Preexhaust
The use of single-joint exercise before multijoint exercises in an effort to exhaust a particular muscle group so that it becomes the weak link in the multijoin exercise.
Primary exercise
An exercise that is most specific to the goals of the lifter. These exercises must involve the muscle groups in which the person is most interested in gaining strength.
Pronation
Rotating the wrist inward.
Pump
A term commonly used by bodybuilders to refer to the swelling that muscles undergo during a workout. The pump occurs because when muscles contract repeatedly they create metabolic waste products that draw water into the muscle. The greater water volume increases the overall size of the muscle cell This can lead to temporary increases in total muscle size of one to two inches. The pump typically lasts until the metabolic waste prod ucts have been cleared from the muscle.
Quads
A slang term referring to the quadriceps muscles on the front thigh.
Range of Motion (ROM)
The range through which a joint can be moved, usually its range of flexion and extension. Exercises also have a specific range of motion that involves the movement from start to finish.
Supplements
Gym Gear
Basic equipment to get for starting up